

The Z-score value can either positive or negative indicating that sample lies above or below the mean by a measure of standard deviations. If the range is smaller the set of data will have a low standard deviation. If the numbers have a large range, or the difference between the largest and smallest value, then it will have a high standard deviation. The standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation in a set of values. A z-score is a way to compare a raw score or data point to the mean, or the average, by using standard deviations. One of the ways that this is done is by the use of the z-score.

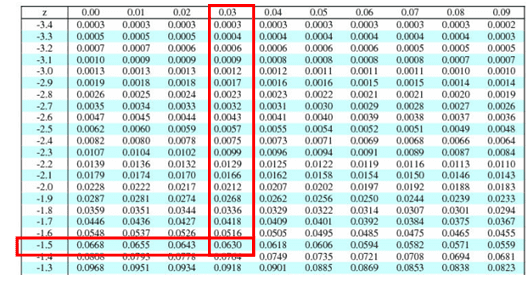
In the world of statistics, numbers and data are gathered, organized and compared in order to derive information and patterns. The Z score itself is a statistical measurement of the number of standard deviations from the mean of a normal distribution. In other words, Z tables help compare data points within a group and show what percentage they are above or below the group average. Z-tables help graphically display the percentage of values above or below a z-score in a group of data or data set. This means that the relative frequency or probability that an event occurs below 1.5 is 0.9332 or 93.32%.Īdjust to Z to find the corresponding probability.Definition: A Z-Score table or chart, often called a standard normal table in statistics, is a math chart used to calculate the area under a normal bell curve for a binomial normal distribution. Knowing that the area under the standard normal distribution is 1: If we refer to the standard normal table it can be observed that for Z = 1.5: We can find the probability of a value being less than 1.5 by finding the area of the blue shaded area below. What is the probability that X is less than 1.5? Let X be a random variable taken from a standard normal distribution. To find the probability value for a z-score of -1, we need to find the area under the standard normal curve between − ∞ and -1. The area under the standard normal distribution curve represents the cumulative probability and as such the total area under the curve is 1. The standard normal distribution has a mean μ = 0, and standard deviation σ = 1. The probability density function of a normal (Gaussian) random variable X is given by:į x = 1 σ ⋅ 2 ⋅ π ⋅ &ExponentialE − x − μ 2 2 ⋅ σ 2
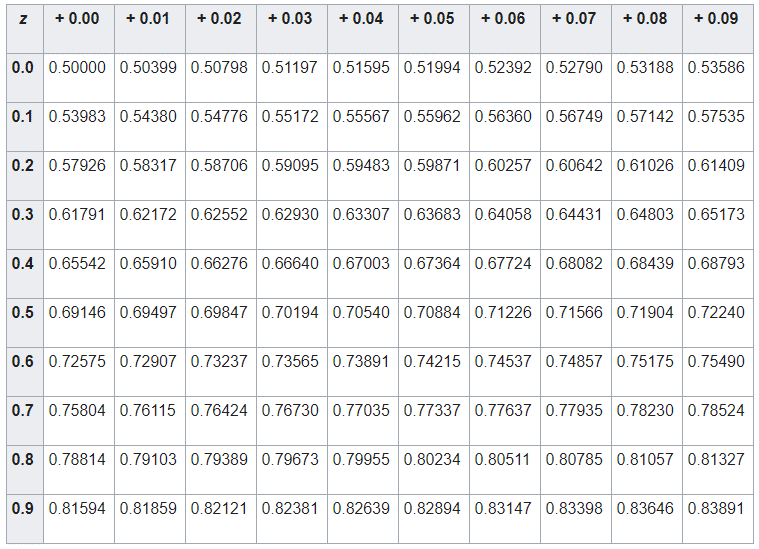
The square root of the variance, &sigma, is called the standard deviation. The variance, &sigma 2, is the expected value of the square of the difference between the value of the X and its mean. For any distribution X, the mean, denoted &mu, is the expected value of X. The values contained in the standard normal distribution table can also be calculated by hand. Once this z-score is known, its respective probability can be looked up in the standard normal distribution table. For more on standardizing data samples, see the Scale command. Z-scores are calculated by first subtracting the mean of the data set from every observation, then dividing by the standard deviation, such that every standardized observation is a measure of how many standard deviations a given observation is from the sample mean. It is common practice to convert any normally distributed data to the standard normal distribution as the standard normal distribution table contains a value for every standardized z-score. More specifically, the table contains values for the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution at a given value, x. A standard normal distribution table, also known as the unit normal table or Z table, is used to find the probability that a statistic is observed below, above, or between values in the standard normal distribution, the so-called p-value.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
